Getting Started
Human subject research (HSR) encompasses both observational and interventional scientific studies involving human participants using quantitative and qualitative research approaches. One can distinguish the following types of human subject research (HSR) along a simple grid:
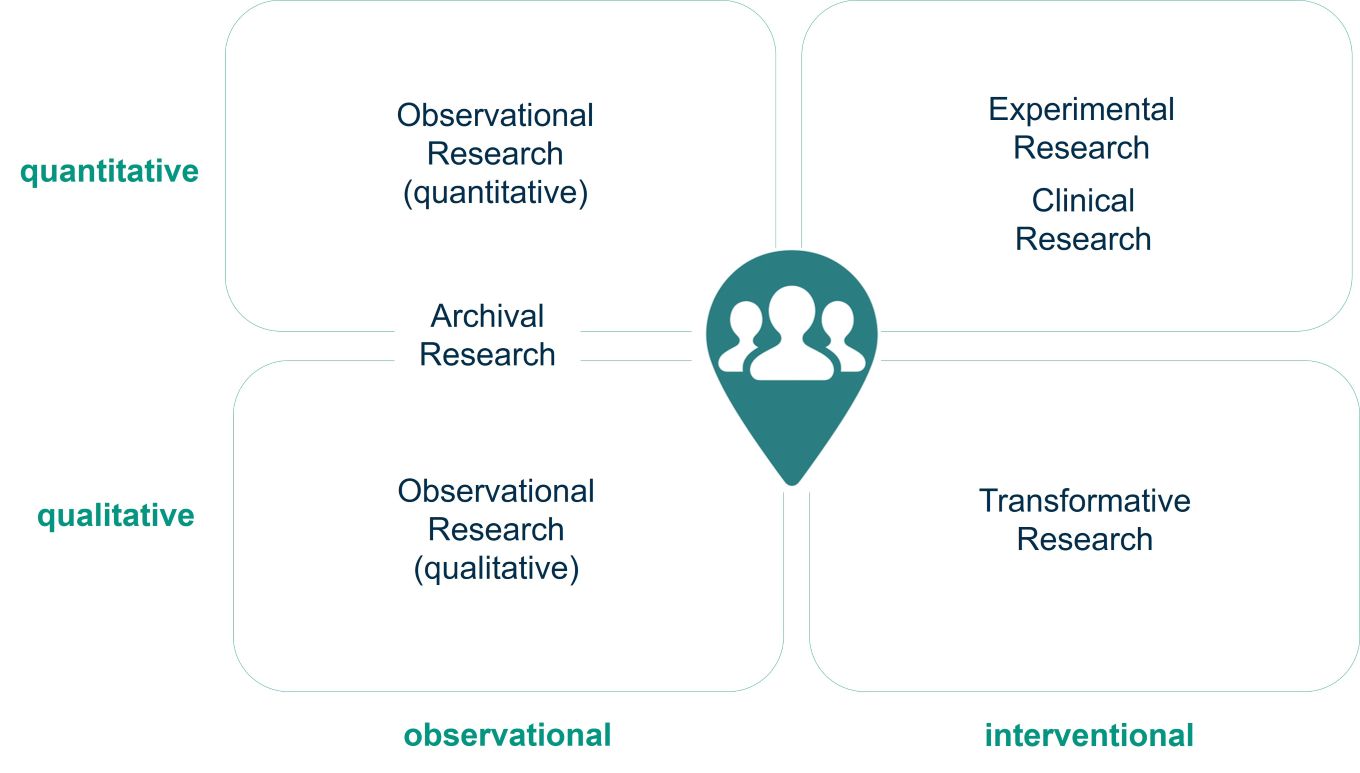
The different types of human subject research (HSR) have their roots in different research disciplines:
Observational HSR:
- Archival Research (rooted in Social Sciences and Economics)
Analyzes existing data - such as social media, public records, or other archives - to identify patterns in human behavior and public discourse over time. Example: Analyzing social media data to study how public discourse evolves. - Observational Research (rooted in Social Sciences)
Collects data throug surveys, interviews, an direct observation to understand opinions, attitudes and behaviors. Approaches used are
quantitative: e.g. large-scale surveyes, qualitative: e.g. interviews, ethnographic observation, or Mixed-methods: combining both.
Example: Conducting interviews to explore satisfaction with a new car design.
Interventional HSR:
- Clinical Research (rooted in Medicine and Life Sciences)
Tests the effectiveness and safety of medical intervention by comparing treatment outcomes to baseline data or control groups.
Example: Evaluation a new drug through a randomized controlled trial. - Experimental Research (rooted Economics, Psychology)
Investigates how controlled interventions influence human behavior and decision-making using lab, online or field experiments.
Example: Using RTCs to study behavioral nudges in sustainable decision-making. - Transformative Research (rooted Social Sciences)
Involves participatory approaches to drive social change, often focusing on community engagement.
Example: Co-developing solutions wiht citizens in a living lab for urban sustainability.
